Bioremediation application summaries are usually done on soils with high levels of contaminants and with highly biodegradable compounds such as fuels or crude oils. Aster Bio has been working on a lab simulation for a site containing soil containing decades old, weathered contamination. The TPH concentrations were approximately 320 mg/kg with the Total Petroleum Hydrocarbon (TPH) fraction present being composed of Poly Aromatic Hydrocarbon (PAH), long chain HCs including asphaltenes, and BTEX levels slightly above 10 mg/kg. From a microbial perspective, this means the readily biodegradable compounds were gone via weathering and native microbial activity. Additionally, the relatively low levels of contaminants make for a more extended and challenging bioremediation project.
Tray Test
To test potential effectiveness of bioremediation, we undertook a tray study to simulate a land farm at ambient conditions. The study included evaluation of a control that received macronutrients, micronutrients, and stimulatory carbon source. The bioaugmented trays received an identical nutrient package plus an inoculum consisting of a consortium of Pseudmonas sp and Rhodococcus sp that have diverse metabolic capabilities and proven effectiveness on PAH and aromatic compounds.
Results at Day 30
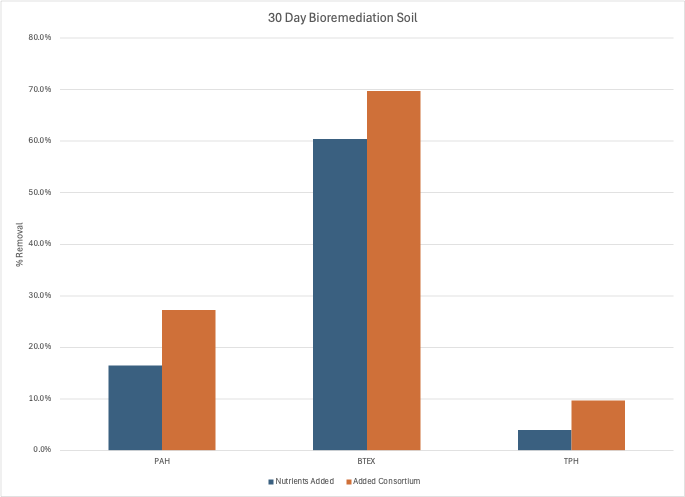
Interpreting Results
The soil had been sitting in storage for decades, leaving recalcitrant compounds at relatively low levels. The bioremediation test shows that BTEX levels drop relatively quickly in a tray study as we provided nutrients and oxygen. The main reason for less than 90%+ degradation was the low levels of BTEX in the sample. With added cultures, the PAH levels dropped by an additional 11% in 30 days compared to the control. TPH being composed of very complex, heavy hydrocarbons was 6% more removed with the added consortium.
Benefits of Bioaugmentation in Soil Remediation
For this application, the remediation will be active with weekly mixing of soils and project staff on site. By reducing time to achieve cleanup, using bioaugmentation cultures can reduce overall project cost and ensure that target degradation rates are met.
